Docker
| Created | |
|---|---|
| Type | Platform |
| Language | Shell |
| Last Edit |
Basics
Platform for building, running and shipping applications.
Docker helps package the required versions of dependencies for an app in an isolated environment called container.
It helps developers to remove an app and all of its dependencies in one go.
Architecture
Container uses underlying OS kernel to run.
Linux: Linux containers can be run.
Windows: Both Windows & Linux containers can be run.
Mac: Requires light weigh Linux VM to run containers.
Development Workflow
Add a docker file to an application to convert application to an image.
Image
It will contain everything an application needs to run.
- Cut down OS
- Runtime environment (eg Node)
- Application files
- Third party libraries
- Environment variables
Container
Docker uses created image to start a container (or process) in an isolated environment.
Docker Hub
Similar to Github for Git.
Once application image is on Docker Hub, we can pull to any machine running docker to run the application
Ubuntu VPS
 https://www.hostinger.com/tutorials/how-to-install-docker-on-ubuntu
https://www.hostinger.com/tutorials/how-to-install-docker-on-ubuntu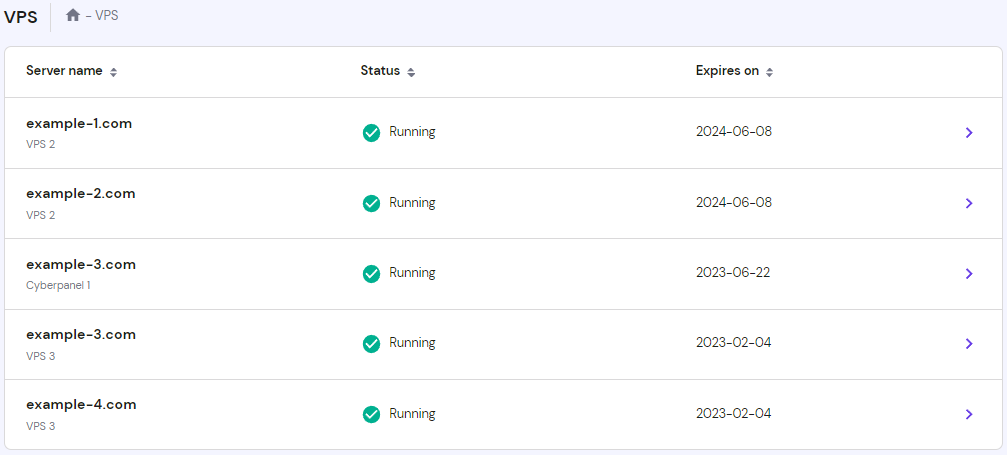
Images Available
Explore Docker's Container Image Repository | Docker Hub
Dockerfile - Best Practices Template
Dockerfiles
Node
 https://github.com/prisma/prisma/discussions/17731
https://github.com/prisma/prisma/discussions/17731Index.js
FROM node:alpine
WORKDIR /app
COPY . /app
CMD node .# syntax=docker/dockerfile:1
# Comments are provided throughout this file to help you get started.
# If you need more help, visit the Dockerfile reference guide at
# https://docs.docker.com/go/dockerfile-reference/
# Want to help us make this template better? Share your feedback here: https://forms.gle/ybq9Krt8jtBL3iCk7
ARG NODE_VERSION=22.11.0
FROM node:${NODE_VERSION}-alpine
# Use production node environment by default.
ENV NODE_ENV production
WORKDIR /usr/src/app
# Download dependencies as a separate step to take advantage of Docker's caching.
# Leverage a cache mount to /root/.npm to speed up subsequent builds.
# Leverage a bind mounts to package.json and package-lock.json to avoid having to copy them into
# into this layer.
RUN --mount=type=bind,source=package.json,target=package.json \
--mount=type=bind,source=package-lock.json,target=package-lock.json \
--mount=type=cache,target=/root/.npm \
npm ci --omit=dev
# Run the application as a non-root user.
USER node
# Copy the rest of the source files into the image.
COPY . .
# Expose the port that the application listens on.
EXPOSE 8001
# Run the application.
CMD npm run api-dev
General dockerfile
FROM node:alpine
WORKDIR /usr/app
COPY package.json .
RUN npm install --quiet
COPY . .Php with apache
FROM php:7.2-apache
COPY src/ /var/www/html/Node on Ubuntu
FROM ubuntu:latest
ENV APP_HOME=/app
ENV NVM_DIR=$APP_HOMEe/.nvm
ARG NODE_VERSION=14.17.3
WORKDIR $APP_HOME
COPY . $APP_HOME
RUN apt-get update \
&& apt-get install -y \
curl \
zip \
unzip \
# && curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_14.x | bash - \
# && apt-get install -y nodejs
# NodeJS
&& mkdir -p ${NVM_DIR} \
&& curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.5/install.sh | bash \
&& . ${NVM_DIR}/nvm.sh \
&& nvm install ${NODE_VERSION} \
&& nvm use v${NODE_VERSION} \
&& npm install -g yarn \
&& nvm alias default v${NODE_VERSION} \
&& rm -rf ${NVM_DIR}/.cache \
&& echo 'export NVM_DIR="/app/.nvm"' >>/app/.bashrc \
&& echo '[ -s "$NVM_DIR/nvm.sh" ] && \. "$NVM_DIR/nvm.sh" # This loads nvm' >>/app/.bashrc \
&& echo '[ -s "$NVM_DIR/bash_completion" ] && \. "$NVM_DIR/bash_completion" # This loads nvm bash_completion' >>/app/.bashrc \
&& npm config set engine-strict true \
&& npm installReact
FROM node:latest
WORKDIR /app
COPY package.json ./
RUN npm install
COPY . .
CMD ["npm", "start"].dockerignore
node_modules
Dockerfile
.gitDjango
Java
RUN apt-get install -y openjdk-8-jdk
RUN apt-get install -y software-properties-common
RUN whereis java
RUN ls /usr/lib/jvm
ENV JAVA_HOME="/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-arm64"
# Verify the installation and environment variable
RUN echo "JAVA_HOME is set to $JAVA_HOME" && \
echo "Java version:" && \
$JAVA_HOME/bin/java -versionKeep Alive
CMD ["tail", "-f", "/dev/null"]Build
Run command inside working directory with Dockerfile
docker build -t image_name:image_tag .Run a specific file for build
docker build -t <image-name>:<tag> -f <Dockerfile-name> <path-to-Dockerfile-directory>Example:
docker build -t clock:service-heroku -f Dockerfile.clock .Clean Up Storage
If required
docker system pruneRun Container
React
docker run --name container_name -d -p 3000:3000 image_name:image_tagWith Hot-Reload
docker run -it --rm -v ${PWD}:/app -v /app/node_modules -e CHOKIDAR_USEPOLLING=true -p 3001:3000 image_name:image_tagAWS
docker run --rm -it amazon/aws-cli commandDocker List
List All Containers
docker container ls -aRunning Containers
docker psDocker Start
docker start containeridDocker Stop
docker stop containeridRunning web server without Dockerfile
Running php and apache
Run this command in terminal inside a repository
docker run -d -p 80:80 --name my-apache-php-app -v "$PWD":/var/www/html php:7.2-apache
Running multiple servers with port mapping
local port ⇒ container port
⚠️ Container port is always 80 unless changed in httpd.conf
docker run -d -p 8000:80 --name my-apache-php-app-2 -v "$PWD":/var/www/html php:7.2-apacheDocker Compose
No Cache
--no-cachedocker compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml build --no-cachedocker-compose.yml
NodeJS
version: "2"
services:
web:
build: .
command: node .
volumes:
- .:/usr/app/
- /usr/app/node_modules
ports:
- "8001:3000"# Comments are provided throughout this file to help you get started.
# If you need more help, visit the Docker Compose reference guide at
# https://docs.docker.com/go/compose-spec-reference/
# Here the instructions define your application as a service called "server".
# This service is built from the Dockerfile in the current directory.
# You can add other services your application may depend on here, such as a
# database or a cache. For examples, see the Awesome Compose repository:
# https://github.com/docker/awesome-compose
services:
server:
build:
context: .
environment:
NODE_ENV: production
ports:
- 8001:8001
# The commented out section below is an example of how to define a PostgreSQL
# database that your application can use. `depends_on` tells Docker Compose to
# start the database before your application. The `db-data` volume persists the
# database data between container restarts. The `db-password` secret is used
# to set the database password. You must create `db/password.txt` and add
# a password of your choosing to it before running `docker-compose up`.
# depends_on:
# db:
# condition: service_healthy
# db:
# image: postgres
# restart: always
# user: postgres
# secrets:
# - db-password
# volumes:
# - db-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
# environment:
# - POSTGRES_DB=example
# - POSTGRES_PASSWORD_FILE=/run/secrets/db-password
# expose:
# - 5432
# healthcheck:
# test: [ "CMD", "pg_isready" ]
# interval: 10s
# timeout: 5s
# retries: 5
# volumes:
# db-data:
# secrets:
# db-password:
# file: db/password.txt
Django
Dev
version: '3.3' services: api: &api container_name: mschool-api build: context: . dockerfile: docker/dev/Dockerfile image: mschool-api command: poetry run python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000 volumes: - .:/app ports: - '${HOST_API_PORT}:8000' env_file: - .env restart: unless-stopped depends_on: - database-pg database-pg: container_name: mschool-db image: postgres restart: always environment: - POSTGRES_DB=${POSTGRES_DB} - POSTGRES_USER=${POSTGRES_USER} - POSTGRES_PASSWORD=${POSTGRES_PASSWORD} - POSTGRES_HOST_AUTH_METHOD=trust volumes: - ./docker/dev/db:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d - postgres-volume:/var/lib/postgresql/data/ ports: - '${POSTGRES_PORT}:5432' env_file: - .env volumes: postgres-volume:
Prod
RUNsed -i 's/\r$//g' /usr/src/app/entrypoint.sh
 https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-build-a-django-and-gunicorn-application-with-docker
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-build-a-django-and-gunicorn-application-with-docker
Redis, Mongo, Celery
There are going to be 5 services in total:
mongodb- for setting up MongoDB
postgres- for setting up PostgreSQL
app- Django project
celery- Queue for tasks
redis- Message broker that required for celery
docker-compose.yml:
version: '3' services: mongo: image: mongo container_name: mongo restart: always env_file: .env environment: - MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=root - MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD=root - MONGO_INITDB_DATABASE=${MONGO_DB_NAME} - MONGO_INITDB_USERNAME=${MONGO_DB_USERNAME} - MONGO_INITDB_PASSWORD=${MONGO_DB_PASSWORD} volumes: - ${PWD}/_data/mongo:/data/db - ${PWD}/docker/_mongo/fixtures:/import - ${PWD}/docker/_mongo/scripts/init.sh:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/setup.sh ports: - 27017:27017 postgres: container_name: postgres image: postgres:12 restart: always env_file: .env environment: - POSTGRES_DB=app_db - POSTGRES_USER=app_db_user - POSTGRES_PASSWORD=supersecretpassword - POSTGRES_PORT=5432 ports: - 5432:5432 volumes: - ${PWD}/_data/postgres:/var/lib/postgresql/data - ${PWD}/docker/_postgres/scripts/create_test_db.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/docker_postgres_init.sql redis: image: redis:6 container_name: redis restart: always env_file: .env command: redis-server --requirepass $REDIS_PASSWORD ports: - 6379:6379 volumes: - ${PWD}/_data/redis:/var/lib/redis app: build: ./app image: app:latest container_name: app restart: always command: "python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000" env_file: .env volumes: - ${PWD}/app:/app ports: - 8000:8000 depends_on: - postgres - redis celery: build: ./app image: app:latest container_name: celery restart: always command: [ "celery", "-A", "app", "worker", "-c", "1", "-l", "INFO", "--without-heartbeat", "--without-gossip", "--without-mingle", ] env_file: .env environment: - DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE=app.settings - DJANGO_WSGI=app.wsgi - DEBUG=False volumes: - ${PWD}/app:/app depends_on: - postgres - redis networks: default:
.env:
# Mongo DB MONGO_DB_HOST=mongo MONGO_DB_PORT=27017 MONGO_DB_NAME=mongo_db MONGO_DB_USERNAME=root MONGO_DB_PASSWORD=root MONGO_DB_URI=mongodb://root:root@mongo:27017 # PostgreSQL POSTGRES_HOST=postgres POSTGRES_DB=app_db POSTGRES_USER=app_db_user POSTGRES_PASSWORD=supersecretpassword POSTGRES_PORT=5432 # Redis REDIS_HOST=redis REDIS_PORT=6379 REDIS_PASSWORD=supersecretpassword BROKER_URL=redis://:supersecretpassword@redis:6379/0 REDIS_CHANNEL_URL=redis://:supersecretpassword@redis:6379/1 CELERY_URL=redis://:supersecretpassword@redis:6379/0
 https://dev.to/thepylot/add-mongodb-and-postgresql-in-django-using-docker-55j6
https://dev.to/thepylot/add-mongodb-and-postgresql-in-django-using-docker-55j6
Execute
Run this command in the current directory with docker-compose.yml
docker compose upCommand to specify docker compose file
docker compose -f docker-compose-local.yml upBuild
docker-compose --build
OR
docker compose -f docker-compose-local.yml up --buildRun
docker-compose up -dSet Memory For Build
docker run -m 4g -it my-docker-imageShutdown
docker compose downShutdown with removing volumes
docker compose down -vEnvironment Variables
Log Env Variables in Container
docker-compose exec db env
docker compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml exec api env Managing Multiple Environments

- .env is for variables that are parsed in to the docker-compose.yml interpreter, not for the container. For variables to be set in the container, you will need to specify a .env file in your docker-compose.yml using
env_file: .env.varsor whatever your file name is that contains the variables. It's a confusing antipattern to useenv_file: .envwhich works but basically uses the variables both for the interpreter and the container. CommentedOct 5, 2022 at 22:56
- 2@bkis It's an anti-pattern because despite appearing to be easier and/or adequate, proper use requires knowledge that is not obvious or well documented, and can lead to confusion (few people are aware that there are actually separate files for the yaml parse and the build part until they run into issues). There are also security concerns; it's generally poor practice to allow variables that are no longer needed to persist through to the final build image/containers. Commented
Don't confuse the
.envfile and theenv_fileoption!They serve totally different purposes!
The
.envfile feeds those environment variables only to your Docker Compose file, which in turn, can be passed to the containers as well.But the
env_fileoption only passes those variables to the containers and not the Docker Compose file
Docker Inspect
Get all details about running container, including Host IP and port.
docker inspect postgresqlDocker Bash
docker exec -it <container-name> sh
docker exec -it <container_name_or_id> bashLogs
docker-compose logs -f
docker logs --tail 100 my-containerDocker Commands Execute
Django
Migrate
docker-compose exec web python manage.py migrateCreate Super User
docker-compose exec web python manage.py createsuperuserDocker Network
Postgres Container
Compose with Health Check
postgres:
image: postgres:13
ports:
- 5432:5432
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: airflow
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: airflow
POSTGRES_DB: airflow
volumes:
- postgres-db-volume:/var/lib/postgresql/data
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "pg_isready", "-U", "airflow"]
interval: 5s
retries: 5
restart: always
Data Initialisation
 https://medium.com/@asuarezaceves/initializing-a-postgresql-database-with-a-dataset-using-docker-compose-a-step-by-step-guide-3feebd5b1545
https://medium.com/@asuarezaceves/initializing-a-postgresql-database-with-a-dataset-using-docker-compose-a-step-by-step-guide-3feebd5b1545
Shell
docker ps
docker exec -it <container_name_or_id> bash
Docker Watch
Use watch to automatically update and preview your running Compose services as you edit and save your code.

Docker Permissions
sudo usermod -a -G docker local
docker (to avoid having to log out and log in again)

